Do you have a world in an older modpack you want to play in a new modpack?
Well I did, so I remapped my world. Specifically, I successfully converted between these major versions:
This is a non-trivial effort, so I figured I would document what I did in case others find it useful.
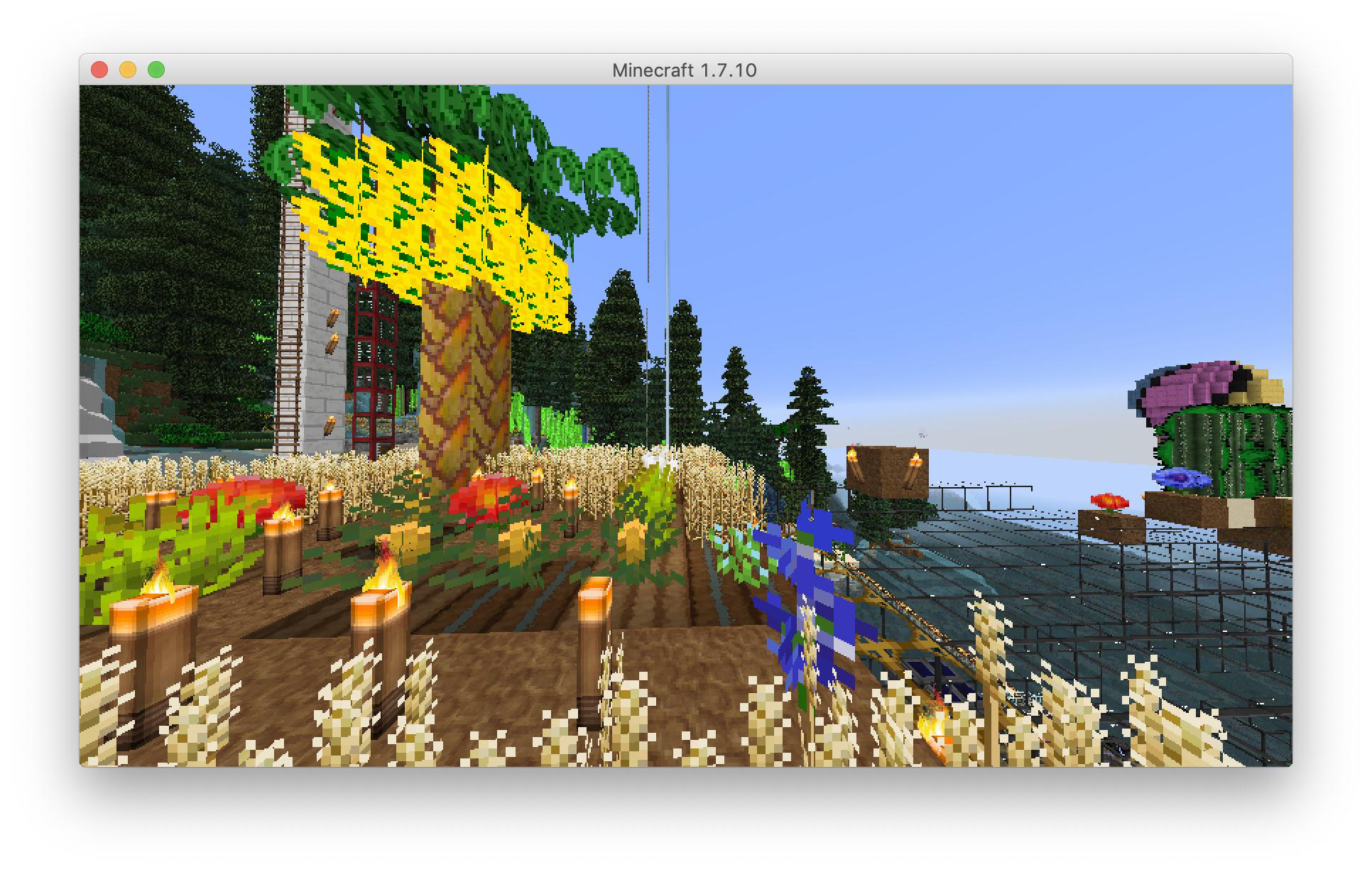
Screenshots, before and after (texture packs are Sphax PureBDcraft and Soartex Modded):

WARNING: Converting worlds between major modded versions is not an exact science. Compromises have to be made and functionality will be lost after the conversion; full-fidelity conversion is not usually feasible because of significant changes between mods across major versions. Furthermore, although the worlds I converted are based on these FTB modpacks, several mods may be removed or added. Your mileage may vary. Make backups!
Disclaimer: For advanced users only. There is not any point-and-click one-step conversion tool, intimate familiarity with programming concepts and Minecraft internals is necessary.
Now that that's out of the way, let's get started.
1. Midas Silver
1.1. Testing loop
1.2. Patchfile Generation: Blocks & Items
1.2.1. ID Dumps
1.2.2. Matching heuristics
1.2.3. Direct and manual mappings
1.2.4. Finding missing mappings
1.2.5. Metadata maps
1.2.6. Overloading multiple substitutions
1.3. Potions, enchantments, and biomes
1.4. Tile entities
2. Patching mods
3. Shifting the world
4. Waypoint conversion
1. Midas Silver
I'll be using Midas Silver, which I forked from Laurence Reading's mIDas GOLD, which in turn was forked by the original mIDas tool developed by Pfaeff. You can checkout the source here: https://github.com/agaricusb/midas-silver.
For now, you have to build it from source yourself, see the instructions in the readme.
The input to this tool is a "patch file", a text file mapping the old IDs to the new IDs. There is one mapping per line, separated by an arrow and an optional comment, for example:
will convert block (or item) ID #200 to #300.
Generating this patchfile is a herculean task and how to do it will cover the bulk of the remainder of this guide and time spent. Before continuing, it is worthwhile to first try running this tool with a small or empty patchfile to get a feeling for how it works. This is the command I use to run a full conversion:
1.1. Testing loop
The basic plan of attack:
For quick iterative testing, if you have a large world, you can copy the crashing region file to a new directory and convert it by itself.
1.2. Patchfile Generation: Blocks & Items
You could write down the old IDs and new IDs and manually match them up, but that will take forever. To expedite the process, we'll dump the IDs and match them up approximately using name matching heuristics.
My patchfile and scripts to generate it, as well as other useful scripts, is available in this repository: https://github.com/agaricusb/WorldRemapping.
1.2.1. ID Dumps
Use Not Enough Items (NEI) to dump the IDs:
On 1.7.10+, the dumps will be stored in CSV format, like this (dumps/block.csv):
On 1.5.2 or earlier, go to NEI Options, Block/Item ID Settings and hit "Dump ID Map Now", the dump will be named like "IDMap_dump-AA152-28-1-2019 at 17.38.21.625.txt" and is in this proprietary dot-deliminated format:
Both ID dump formats are easily parsed and are supported by the tools described next.
1.2.2. Matching heuristics
The basic strategy will be to match up the names from the old dump to the newer. Names are not always sufficient, so configuration files will also be parsed. To implement this technique I whipped up a quick script match-ids.py in the WorldRemapping repo, you give it two ID dumps, two config directories, and it compares the two and generates a patchfile. Example usage:
match-ids.py is a collection of heuristics and hacks intended to remap the world as closely as possible. It is highly specific to my worlds, so it will need to be edited for yours. Here's some tips on matching:
Exact match: Identical name in old and new. This can occur if remapping between similar versions, but is doesn't occur between say 1.5/7.
Replacement match: Strip the "item." and "tile." prefixes and attempt an anyspace match. "tile.stone" for example matches "minecraft:stone".
Namespace match: If the old version had a fake namespace, like "tile.bop.", then we can try replacing it with a real namespace, "BiomesOPlenty:". This matches 459 blocks or items in my world. Edit replacePrefixes to map the replacements, for example:
Casing adjustments: Mystcraft now upper-cases the first letter of its IDs, and Tinkers' Construct lowercases the first letter. The script hardcodes these casing adjustments:
Snake case is also converted (fooBar is replaced with foo_bar).
Unprefix match: IC2 names items beginning with "item", but without a dot for some reason. 165 of these match, example:
Anyspace match: Search all namespaces (the foo in foo:bar) for the old name. This finds 852 in my world, a very useful heuristic. To avoid ambiguities, if more than one namespace matches the old name, it is excluded.
Config match: Search the config files for possible ID assignments, parsing (\w+)=(\d+) regex and matching on the identifier. This was useful in my 1.5.2 from 1.2.5 conversion, but wasn't used in 1.7.10 from 1.5.2.
No match: If no match can be found, then the mapping is emitted but commented-out and marked 'no match'.
1.2.3. Direct and manual mappings
Heuristics can only go so far. There will be missing mappings.
Sometimes, you'll have no choice but to load up both games and find the same item in both instances. Find their name in the ID dumps and add it to the "manual" dictionary. I have an extensive set of 600+ manual mappings, such as:
which accounts for 528 translations. You can also add approximate substitutions here (see below).
Using the item name is preferred if possible, to avoid dependence on the fixed numeric ID, but this is not always possible. For example, Obsidian Pressure Plates had this identifier:
"tile.null" is ambiguous. To handle these cases, add the old numeric ID and new string ID and a comment to the "direct" dictionary:
This will break if you have different numeric IDs in your world than mine, so be sure to edit it as needed.
1.2.4. Finding missing mappings
Not all IDs have to be converted, if they are not used in the world. To find the missing mappings that actually matter, Midas Silver supports the --warn-unconverted-block-id-after 158 and --warn-unconverted-item-id-after 408 flags. Pass the vanilla IDs to those flags, since vanilla doesn't need to be converted.
"untranslated item: " and "untranslated block: " will be logged for each time an unmapped ID is encountered. Grep for untranslated and count the frequency of each ID to determine what is important to convert next:
If everything non-vanilla is translated, then only the record item IDs will be logged (since they are non-contiguous):
You can also count the IDs that were actually translated using the --count-block-stats and --count-item-stats flags, to determine how important it is to choose a reasonable replacement.
1.2.5. Metadata maps
By default, the block metadata and item damage values are preserved.
If necessary, both Midas Silver and WorldRemapping can remap metadata. This is useful if the metadata changed between versions, or if preserving the metadata causes crashes. Add to the "metadata_map" dictionary, example for Forgotten Nature:
is emitted in patchfile.txt as:
1.2.6. Overloading multiple substitutions
What if a mod is removed, or significantly refactored so that blocks/items are no longer available? Leaving the untranslated IDs in the world may cause crashes, really everything has to be translated if you want a reliable world.
You can use manual mappings to add approximate substitutions. But WorldRemapping won't allow multiple assignments by default, that is, all mappings have to be 1:1 not 1:n. This can be overridden by adding the name to overloaded_allow_multiple_substitutions. If the block/item you want to substitute is in vanilla (such as minecraft:air), then also add to force_available_substitutions.
Example of how I use overloaded substitutions, added to "manual":
added to overload list:
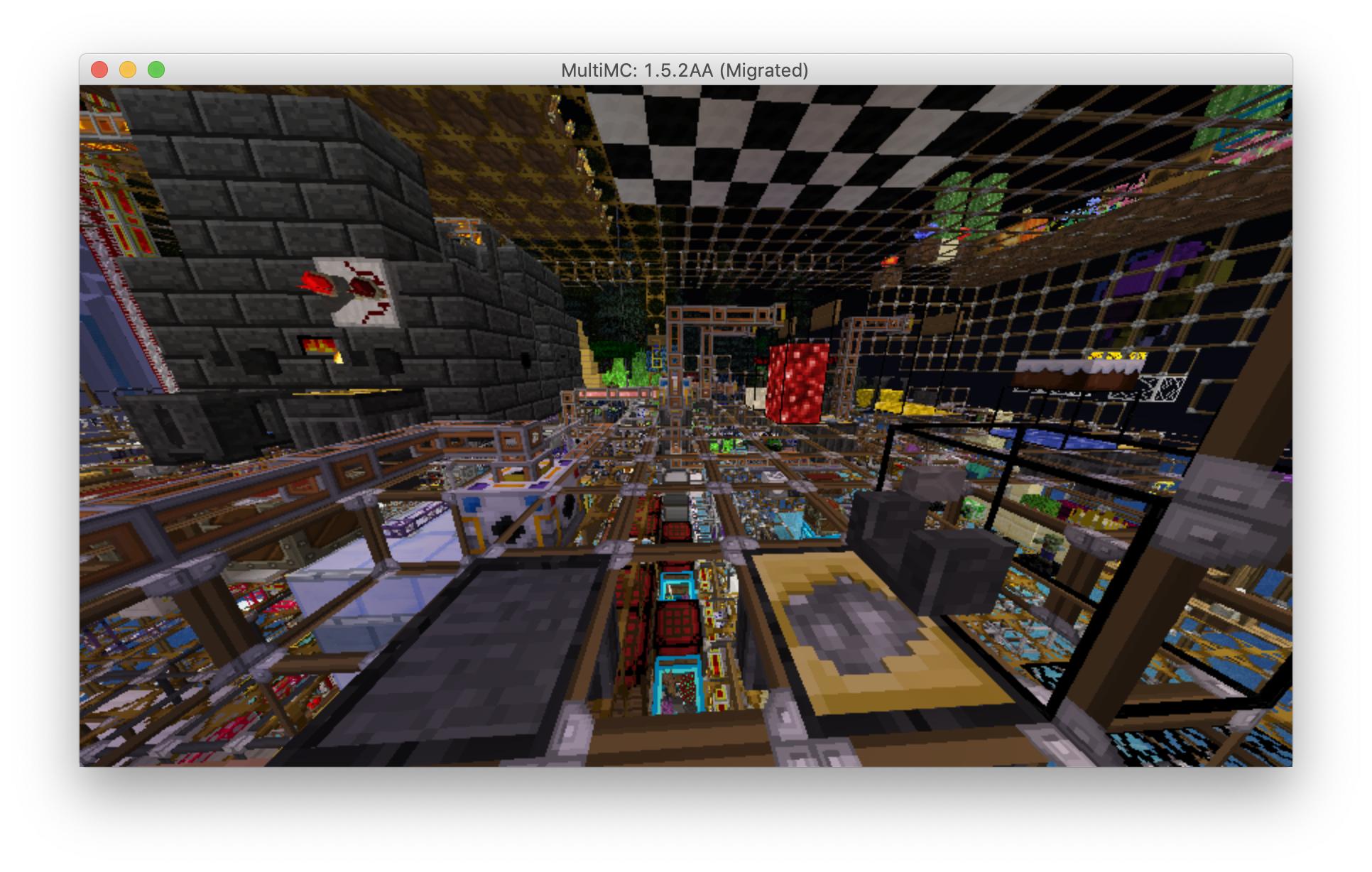
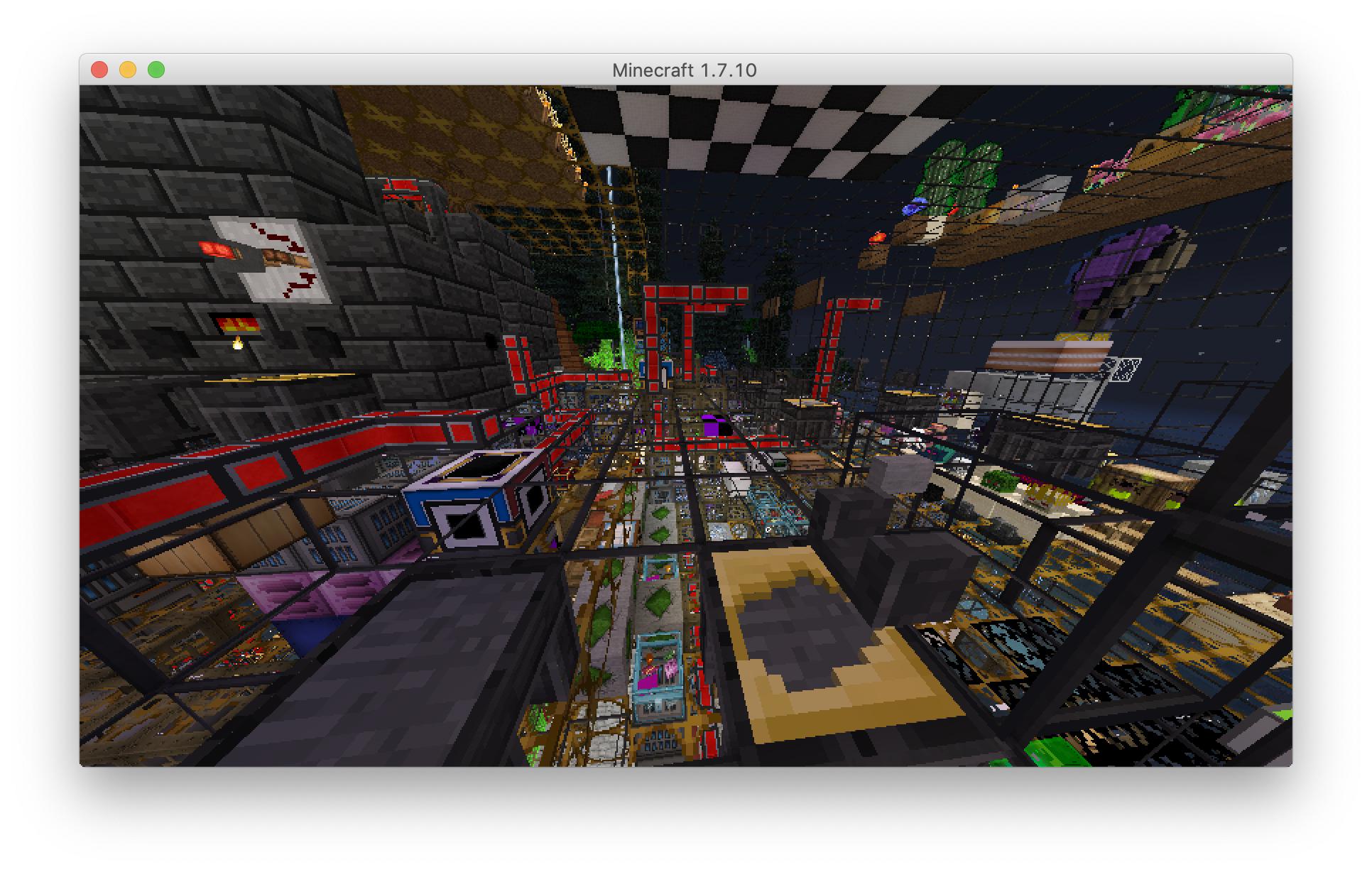
Here is another screenshot of my converted world, a more complex area which was partially converted (notice the checkered purple/black "missing block" texture near the center), but is generally recognizable:
1.3. Potions, enchantments, and biomes
Although biomes, enchantments, and potions have IDs, in practice using the wrong IDs doesn't seem to cause crashes, so I did not bother to convert them. YMMV.
1.4. Tile entities
Now you have blocks and items converted, there is another piece of world data that can change: tile entities. This named binary tag (NBT) is used to store extra information about interactive blocks, such as storage chests or machines.
Midas Silver (and mIDas GOLD) will automatically convert item IDs in chest TE's.
"--dump-tile-entities" can be used to dump all the TE NBTs for analysis. Review the old structure and write code to convert to the new structure in Midas Silver itself. Currently two built-in plugins are supported:
* --convert-project-table: RedPower2 Project Table to bau5 Project Bench
* --convert-charging-bench-gregtech: IC2 Charging Bench to GregTech Charge-O-Mat
These are both for converting to 1.5.2 from 1.2.5, and were not used for 1.7.10 from 1.5.2. It is possible, but reaches the point of diminishing returns: developing TE conversion plugins is a lot of work for minimal benefit (you get to keep your items), but the option is there if you want it.
Alternatively, leave unconverted and let Forge remove any broken entities, config/forge.cfg:
Cheating in any broken machines may be more practical than writing the conversion code, but if you do write any converter plugins feel free to submit pull requests to midas-silver.
2. Patching mods
Ideally the old world can be converted into a completely valid new world, but this is easier said than done. Mods do not always handle invalid data they do not expect, and can annoyingly crash the client or server.
As a last resort, you can patch the mods to fix the crashes. This works well if the cause of the crash is obvious, such as an AIOOB:
This is a crash in Forgotten Nature version 1.7.19 (ForgottenNature_1.7.19old.jar), when a fruit item is rendered with metadata. Metadata maps could convert to valid metadata in theory, but remapping everything becomes too cumbersome, in some cases it can be easier to patch it out.
Decompile the mod with Fernflower, or another Java decompiler. Recompile against a deobfuscated Minecraft jar and Forge. This is the fix I used for the ItemFruit crash:
Storyyeller's Krakatau Bytecode Tools may also be useful for mod patching, if the decompile/recompile process is too difficult.
To apply the patch, you can either use my Jarmod2Coremod, or modify the mod jar replacing the class file (but be mindful of redistribution concerns if you run a public server).
3. Shifting the world
As part of converting the old world, I wanted to merge it into my existing new world. After all, it took a while to complete the conversion (about a month of work writing the patchfile, about an hour to run, started years after I updated) so I was playing on the latest and greatest version of modded Minecraft, 1.7.10, the version with the most mods, and wanted to preserve my new 1.7.10-only world within the 1.5.2-to-1.7.10 world (leaving behind the days of MCPC+).
My initial attempt was to rename the region files, r.0.0.mca to r.20.0.mca (etc). See Dinnerbone Coordinate Tools for what blocks and chunks are in each region. Multiplying by 512, region 20.0 corresponds to x=10240, z=0.
Renaming the region files is necessary, but not sufficient. Why not? Regions contain embedded coordinates, and these also have to be updated. To do this, if your world is small enough you could try MCEdit, but I wanted a simpler command-line tool, so I used the same underlying library mcedit uses, pymclevel, and wrote what I call shiftmca. It can efficiently shift the region's X coordinate by any amount, while leaving Y and Z intact.
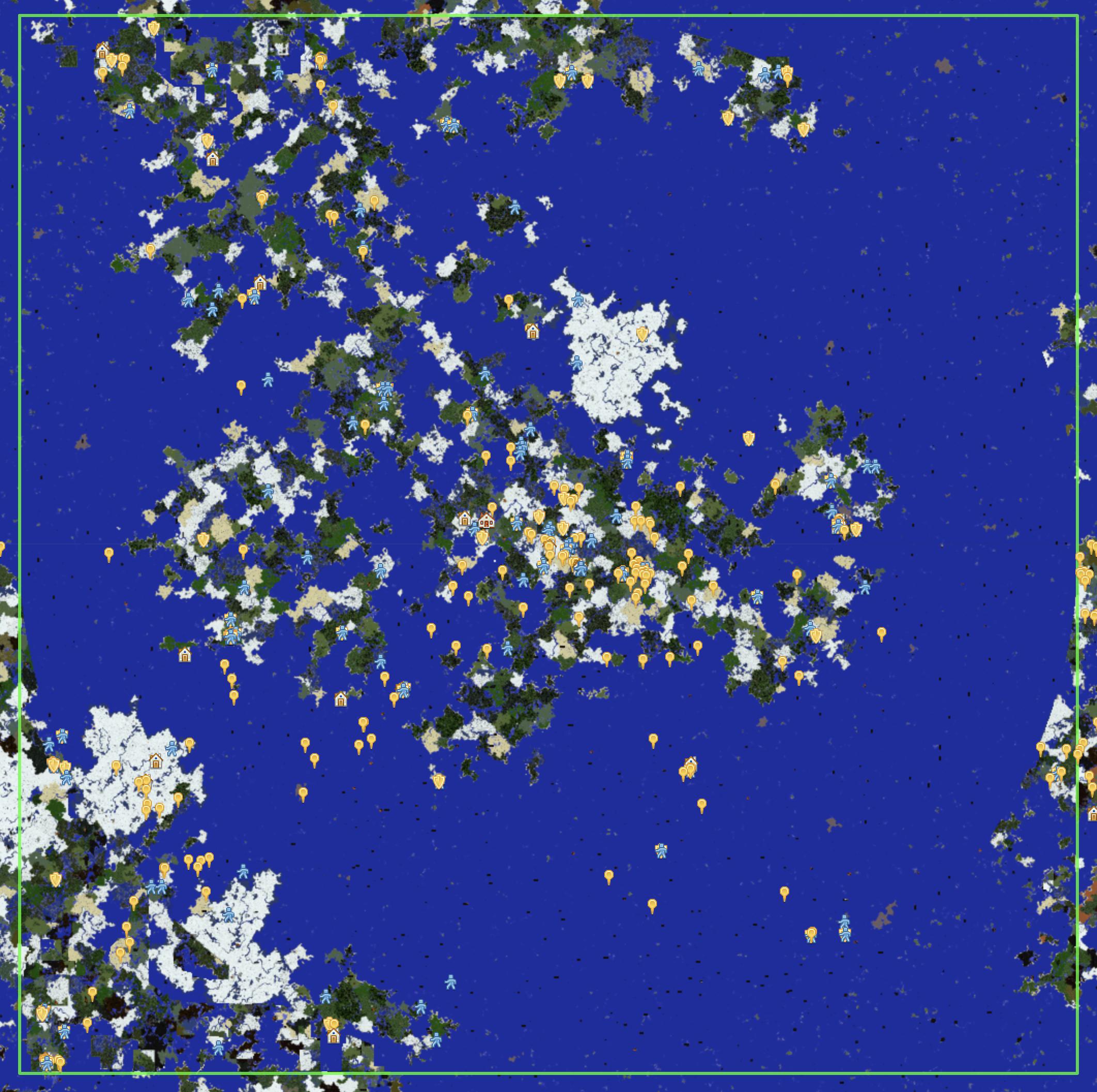
I have several maps with a rich lineage merged into one unified world. shiftmca was used in my modded world conversion, but I also used it to add a copy of HardcoreSMP World 3 (2011-2012), a 20,000 x 20,000 vanilla Minecraft 1.0.0 world from the days of yore. To clearly delinate the imported world, Dynmap's area markers are useful:
Example screenshot of the converted and merged modded 1.5.2 world in modded 1.7.10, with the boundary:
4. Waypoint conversion
In WorldRemapping there are several handy scripts to convert waypoints:
* wp_rei2journeymap.py: convert Rei's Minimap to Journeymap (note: Journeymap also has its own Rei Minimap importer, try it instead)
* journeymap2dynmap.py: convert Journeymap waypoints to Dynmap markers
* player2wp: convert player.dat spawn and logout locations to Journeymap waypoints
The latter is particularly useful if you are importing a large public server and want to see where everyone was. These tools take into account the region shift from shiftmca.
Well I did, so I remapped my world. Specifically, I successfully converted between these major versions:
- Modded 1.7.10 from 1.5.2 (i.e., FTB Infinity Evolved era from FTB Unleashed/Unhinged era)
- Modded 1.5.2 from 1.2.5 (FTB Unleashed/Unhinged era from FTB Retro/Tekkit era)
This is a non-trivial effort, so I figured I would document what I did in case others find it useful.
Screenshots, before and after (texture packs are Sphax PureBDcraft and Soartex Modded):


WARNING: Converting worlds between major modded versions is not an exact science. Compromises have to be made and functionality will be lost after the conversion; full-fidelity conversion is not usually feasible because of significant changes between mods across major versions. Furthermore, although the worlds I converted are based on these FTB modpacks, several mods may be removed or added. Your mileage may vary. Make backups!
Disclaimer: For advanced users only. There is not any point-and-click one-step conversion tool, intimate familiarity with programming concepts and Minecraft internals is necessary.
Now that that's out of the way, let's get started.
1. Midas Silver
1.1. Testing loop
1.2. Patchfile Generation: Blocks & Items
1.2.1. ID Dumps
1.2.2. Matching heuristics
1.2.3. Direct and manual mappings
1.2.4. Finding missing mappings
1.2.5. Metadata maps
1.2.6. Overloading multiple substitutions
1.3. Potions, enchantments, and biomes
1.4. Tile entities
2. Patching mods
3. Shifting the world
4. Waypoint conversion
1. Midas Silver
I'll be using Midas Silver, which I forked from Laurence Reading's mIDas GOLD, which in turn was forked by the original mIDas tool developed by Pfaeff. You can checkout the source here: https://github.com/agaricusb/midas-silver.
For now, you have to build it from source yourself, see the instructions in the readme.
The input to this tool is a "patch file", a text file mapping the old IDs to the new IDs. There is one mapping per line, separated by an arrow and an optional comment, for example:
Code:
200 -> 300 # commentwill convert block (or item) ID #200 to #300.
Generating this patchfile is a herculean task and how to do it will cover the bulk of the remainder of this guide and time spent. Before continuing, it is worthwhile to first try running this tool with a small or empty patchfile to get a feeling for how it works. This is the command I use to run a full conversion:
Code:
cp -vr ~/minecraft/1.4.x/real-152-server/world/players/ ~/minecraft/1710/modpack/staging-server/world/players/
cp -vr ~/minecraft/1.4.x/real-152-server/world/region/ ~/minecraft/1710/modpack/staging-server/world/region/
time java -jar target/midas-silver-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar --patch-file ../WorldRemapping/patchfile.txt \
--input-save-game ~/minecraft/1710/modpack/staging-server/world \
--warn-unconverted-block-id-after 158 \
--warn-unconverted-item-id-after 408 \
--count-block-stats \
--count-item-stats \
--dump-tile-entities \
| tee /tmp/out1.1. Testing loop
The basic plan of attack:
- Run the conversion
- Load up the world
- Play until crashes
- Fix
- Repeat
For quick iterative testing, if you have a large world, you can copy the crashing region file to a new directory and convert it by itself.
1.2. Patchfile Generation: Blocks & Items
You could write down the old IDs and new IDs and manually match them up, but that will take forever. To expedite the process, we'll dump the IDs and match them up approximately using name matching heuristics.
My patchfile and scripts to generate it, as well as other useful scripts, is available in this repository: https://github.com/agaricusb/WorldRemapping.
1.2.1. ID Dumps
Use Not Enough Items (NEI) to dump the IDs:
- Open the inventory (press E)
- Go to Options
- Go to Tools
- Go to Data Dumps
- Click "Dump" under Items and Blocks
On 1.7.10+, the dumps will be stored in CSV format, like this (dumps/block.csv):
Code:
Name,ID,Has Item,Mod,Class
minecraft:air,0,false,null,net.minecraft.block.BlockAir
minecraft:stone,1,true,null,net.minecraft.block.BlockStone
minecraft:grass,2,true,null,net.minecraft.block.BlockGrass
minecraft:dirt,3,true,null,net.minecraft.block.BlockDirtOn 1.5.2 or earlier, go to NEI Options, Block/Item ID Settings and hit "Dump ID Map Now", the dump will be named like "IDMap_dump-AA152-28-1-2019 at 17.38.21.625.txt" and is in this proprietary dot-deliminated format:
Code:
Block. Name: tile.stone. ID: 1
Block. Name: tile.grass. ID: 2
Block. Name: tile.dirt. ID: 3Both ID dump formats are easily parsed and are supported by the tools described next.
1.2.2. Matching heuristics
The basic strategy will be to match up the names from the old dump to the newer. Names are not always sufficient, so configuration files will also be parsed. To implement this technique I whipped up a quick script match-ids.py in the WorldRemapping repo, you give it two ID dumps, two config directories, and it compares the two and generates a patchfile. Example usage:
Code:
python match-ids.py IDMap_dump-AA152-28-1-2019\ at\ 17.38.21.625.txt 1710-dumps /Applications/MultiMC.app/Contents/MacOS/instances/1.5.2AA\ \(Migrated\)1/minecraft/config/ /Applications/MultiMC.app/Contents/MacOS/instances/1.7.10s/minecraft/config > patchfile.txtmatch-ids.py is a collection of heuristics and hacks intended to remap the world as closely as possible. It is highly specific to my worlds, so it will need to be edited for yours. Here's some tips on matching:
Exact match: Identical name in old and new. This can occur if remapping between similar versions, but is doesn't occur between say 1.5/7.
Replacement match: Strip the "item." and "tile." prefixes and attempt an anyspace match. "tile.stone" for example matches "minecraft:stone".
Namespace match: If the old version had a fake namespace, like "tile.bop.", then we can try replacing it with a real namespace, "BiomesOPlenty:". This matches 459 blocks or items in my world. Edit replacePrefixes to map the replacements, for example:
- "tile.bop.": "BiomesOPlenty:", "item.bop.": "BiomesOPlenty:",
- "tile.extrabiomes.": "ExtrabiomesXL:",
- "tile.immibis/redlogic:": "RedLogic:redlogic.",
- "item.AppEng.": "appliedenergistics2:item.", "tile.AppEng.": "appliedenergistics2:tile.",
- "tile.railcraft.": "Railcraft:", "item.railcraft.": "Railcraft:",
Casing adjustments: Mystcraft now upper-cases the first letter of its IDs, and Tinkers' Construct lowercases the first letter. The script hardcodes these casing adjustments:
Code:
if newName.startswith("Mystcraft:"): newName = n[0] + ":" + "Block" + ucfirst(n[1])
if newName.startswith("TConstruct:"): newName = n[0] + ":" + lcfirst(n[1])
if newName.startswith("atum:"): newName = n[0] + ":" + m[0] + "." + lcfirst(m[1])
if newName.startswith("ThermalExpansion:"): newName = n[0] + ":" + ucfirst(n[1])Snake case is also converted (fooBar is replaced with foo_bar).
Unprefix match: IC2 names items beginning with "item", but without a dot for some reason. 165 of these match, example:
Code:
30242 -> 4236 # ('itemBatRE', 'IC2:itemBatRE', 'unprefix')Anyspace match: Search all namespaces (the foo in foo:bar) for the old name. This finds 852 in my world, a very useful heuristic. To avoid ambiguities, if more than one namespace matches the old name, it is excluded.
Config match: Search the config files for possible ID assignments, parsing (\w+)=(\d+) regex and matching on the identifier. This was useful in my 1.5.2 from 1.2.5 conversion, but wasn't used in 1.7.10 from 1.5.2.
No match: If no match can be found, then the mapping is emitted but commented-out and marked 'no match'.
1.2.3. Direct and manual mappings
Heuristics can only go so far. There will be missing mappings.
Sometimes, you'll have no choice but to load up both games and find the same item in both instances. Find their name in the ID dumps and add it to the "manual" dictionary. I have an extensive set of 600+ manual mappings, such as:
Code:
"tile.IronChest": "IronChest:BlockIronChest",
"tile.CompactSolar": "CompactSolars:CompactSolarBlock",
# Mo' Creatures
"item.moc_egg": "MoCreatures:mocegg",
"item.turtlemeat": "MoCreatures:turtleraw",
"item.key": "MoCreatures:key",
"item.furplate": "MoCreatures:furchest",which accounts for 528 translations. You can also add approximate substitutions here (see below).
Using the item name is preferred if possible, to avoid dependence on the fixed numeric ID, but this is not always possible. For example, Obsidian Pressure Plates had this identifier:
Code:
Block. Name: tile.null. ID: 1555"tile.null" is ambiguous. To handle these cases, add the old numeric ID and new string ID and a comment to the "direct" dictionary:
Code:
1555: ("ObsidiPlates:ObsidianPressurePlate", "ObsidiPlates obsidianPlate"),This will break if you have different numeric IDs in your world than mine, so be sure to edit it as needed.
1.2.4. Finding missing mappings
Not all IDs have to be converted, if they are not used in the world. To find the missing mappings that actually matter, Midas Silver supports the --warn-unconverted-block-id-after 158 and --warn-unconverted-item-id-after 408 flags. Pass the vanilla IDs to those flags, since vanilla doesn't need to be converted.
"untranslated item: " and "untranslated block: " will be logged for each time an unmapped ID is encountered. Grep for untranslated and count the frequency of each ID to determine what is important to convert next:
Code:
grep untranslated out | perl -MData::Dumper -ne'$f{$_}++}; END { print Dumper \%f; } {'If everything non-vanilla is translated, then only the record item IDs will be logged (since they are non-contiguous):
Code:
$VAR1 = {
'untranslated item:2262:0
' => 4,
'untranslated item:2259:0
' => 2,
'untranslated item:2257:0
' => 18
};You can also count the IDs that were actually translated using the --count-block-stats and --count-item-stats flags, to determine how important it is to choose a reasonable replacement.
1.2.5. Metadata maps
By default, the block metadata and item damage values are preserved.
If necessary, both Midas Silver and WorldRemapping can remap metadata. This is useful if the metadata changed between versions, or if preserving the metadata causes crashes. Add to the "metadata_map" dictionary, example for Forgotten Nature:
Code:
"tile.Crystal Mushroom Block":
{
# old_meta: new_meta
0: 0,
1: 0,
},is emitted in patchfile.txt as:
Code:
2561:0 -> 3764:0 # ('tile.Crystal Mushroom Block', 'ForgottenNature:cMushroomBlock', 'manual') (META)
2561:1 -> 3764:0 # ('tile.Crystal Mushroom Block', 'ForgottenNature:cMushroomBlock', 'manual') (META)1.2.6. Overloading multiple substitutions
What if a mod is removed, or significantly refactored so that blocks/items are no longer available? Leaving the untranslated IDs in the world may cause crashes, really everything has to be translated if you want a reliable world.
You can use manual mappings to add approximate substitutions. But WorldRemapping won't allow multiple assignments by default, that is, all mappings have to be 1:1 not 1:n. This can be overridden by adding the name to overloaded_allow_multiple_substitutions. If the block/item you want to substitute is in vanilla (such as minecraft:air), then also add to force_available_substitutions.
Example of how I use overloaded substitutions, added to "manual":
Code:
# Dartcraft substitutions
"tile.hive_": "ihl:oreBischofite",
"tile.powerOre": "ihl:oreMica",
"tile.forceStairs": "ForgottenNature:FNWStairs1",
"tile.forceLog": "ExtrabiomesXL:log1",
"tile.forceLeaves": "ExtrabiomesXL:leaves_1",
"tile.forceSapling": "ExtrabiomesXL:saplings_1",added to overload list:
Code:
overloaded_allow_multiple_substitutions = [
"ForgottenNature:FNWStairs1",
"ExtrabiomesXL:log1",
"ExtrabiomesXL:leaves_1",
"ExtrabiomesXL:leaves_2",
"ExtrabiomesXL:saplings_1",Here is another screenshot of my converted world, a more complex area which was partially converted (notice the checkered purple/black "missing block" texture near the center), but is generally recognizable:


1.3. Potions, enchantments, and biomes
Although biomes, enchantments, and potions have IDs, in practice using the wrong IDs doesn't seem to cause crashes, so I did not bother to convert them. YMMV.
1.4. Tile entities
Now you have blocks and items converted, there is another piece of world data that can change: tile entities. This named binary tag (NBT) is used to store extra information about interactive blocks, such as storage chests or machines.
Midas Silver (and mIDas GOLD) will automatically convert item IDs in chest TE's.
"--dump-tile-entities" can be used to dump all the TE NBTs for analysis. Review the old structure and write code to convert to the new structure in Midas Silver itself. Currently two built-in plugins are supported:
* --convert-project-table: RedPower2 Project Table to bau5 Project Bench
* --convert-charging-bench-gregtech: IC2 Charging Bench to GregTech Charge-O-Mat
These are both for converting to 1.5.2 from 1.2.5, and were not used for 1.7.10 from 1.5.2. It is possible, but reaches the point of diminishing returns: developing TE conversion plugins is a lot of work for minimal benefit (you get to keep your items), but the option is there if you want it.
Alternatively, leave unconverted and let Forge remove any broken entities, config/forge.cfg:
Code:
# Set this to true to remove any Entity that throws an error in its update method instead of closing the server and reporting a crash log. BE WARNED THIS COULD SCREW UP EVERYTHING USE SPARINGLY WE ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR DAMAGES.
B:removeErroringEntities=false
# Set this to true to remove any TileEntity that throws an error in its update method instead of closing the server and reporting a crash log. BE WARNED THIS COULD SCREW UP EVERYTHING USE SPARINGLY WE ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR DAMAGES.
B:removeErroringTileEntities=falseCheating in any broken machines may be more practical than writing the conversion code, but if you do write any converter plugins feel free to submit pull requests to midas-silver.
2. Patching mods
Ideally the old world can be converted into a completely valid new world, but this is easier said than done. Mods do not always handle invalid data they do not expect, and can annoyingly crash the client or server.
As a last resort, you can patch the mods to fix the crashes. This works well if the cause of the crash is obvious, such as an AIOOB:
Code:
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 15
at ForgottenNature.Items.ItemFruit.func_77667_c(ItemFruit.java:38)
at net.minecraft.item.ItemStack.func_77977_a(ItemStack.java:361)
at jds.bibliocraft.rendering.TileEntityWeaponRackRenderer.renderRackSlot(TileEntityWeaponRackRenderer.java:200)
at jds.bibliocraft.rendering.TileEntityWeaponRackRenderer.func_147500_a(TileEntityWeaponRackRenderer.java:189)
at net.minecraft.client.renderer.tileentity.TileEntityRendererDispatcher.func_147549_a(SourceFile:100)
at net.minecraft.client.renderer.tileentity.TileEntityRendererDispatcher.func_147544_a(SourceFile:92)This is a crash in Forgotten Nature version 1.7.19 (ForgottenNature_1.7.19old.jar), when a fruit item is rendered with metadata. Metadata maps could convert to valid metadata in theory, but remapping everything becomes too cumbersome, in some cases it can be easier to patch it out.
Decompile the mod with Fernflower, or another Java decompiler. Recompile against a deobfuscated Minecraft jar and Forge. This is the fix I used for the ItemFruit crash:
Code:
--- a/ForgottenNature/Items/ItemFruit.java
+++ b/ForgottenNature/Items/ItemFruit.java
@@ -28,11 +28,13 @@ public class ItemFruit extends ItemFood {
public String func_77667_c(ItemStack p_71) {
int i = MathHelper.func_76125_a(p_71.func_77960_j(), 0, 15);
+ i %= names.length;
return super.func_77658_a() + "." + names[i];
}
@SideOnly(Side.CLIENT)
public IIcon func_77617_a(int i) {
+ i %= this.fruitIcons.length;
return this.fruitIcons[i];
}Storyyeller's Krakatau Bytecode Tools may also be useful for mod patching, if the decompile/recompile process is too difficult.
To apply the patch, you can either use my Jarmod2Coremod, or modify the mod jar replacing the class file (but be mindful of redistribution concerns if you run a public server).
3. Shifting the world
As part of converting the old world, I wanted to merge it into my existing new world. After all, it took a while to complete the conversion (about a month of work writing the patchfile, about an hour to run, started years after I updated) so I was playing on the latest and greatest version of modded Minecraft, 1.7.10, the version with the most mods, and wanted to preserve my new 1.7.10-only world within the 1.5.2-to-1.7.10 world (leaving behind the days of MCPC+).
My initial attempt was to rename the region files, r.0.0.mca to r.20.0.mca (etc). See Dinnerbone Coordinate Tools for what blocks and chunks are in each region. Multiplying by 512, region 20.0 corresponds to x=10240, z=0.
Renaming the region files is necessary, but not sufficient. Why not? Regions contain embedded coordinates, and these also have to be updated. To do this, if your world is small enough you could try MCEdit, but I wanted a simpler command-line tool, so I used the same underlying library mcedit uses, pymclevel, and wrote what I call shiftmca. It can efficiently shift the region's X coordinate by any amount, while leaving Y and Z intact.
I have several maps with a rich lineage merged into one unified world. shiftmca was used in my modded world conversion, but I also used it to add a copy of HardcoreSMP World 3 (2011-2012), a 20,000 x 20,000 vanilla Minecraft 1.0.0 world from the days of yore. To clearly delinate the imported world, Dynmap's area markers are useful:
Code:
/dmarker addcorner 10992 65 -10000 world
/dmarker addcorner 30992 65 10000
/dmarker addarea hcsmp
/dmarker updatearea hcsmp fillopacity:0.0
set the boundary to the build limit, of +/-10k for 20,000 x 20,000Example screenshot of the converted and merged modded 1.5.2 world in modded 1.7.10, with the boundary:

4. Waypoint conversion
In WorldRemapping there are several handy scripts to convert waypoints:
* wp_rei2journeymap.py: convert Rei's Minimap to Journeymap (note: Journeymap also has its own Rei Minimap importer, try it instead)
* journeymap2dynmap.py: convert Journeymap waypoints to Dynmap markers
* player2wp: convert player.dat spawn and logout locations to Journeymap waypoints
The latter is particularly useful if you are importing a large public server and want to see where everyone was. These tools take into account the region shift from shiftmca.